Radio over IP (RoIP) via Satellite
Voice over IP (VoIP) allows us to use the Internet to relay a telephone call. There are many VoIP software and hardware solutions that can effectively replace plain old telephone service (POTS).
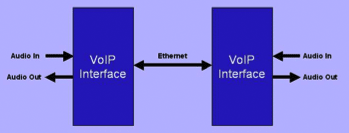
Radio over IP (RoIP) is a more elaborate form of VoIP. To establish a link between a radio console (the end user's 2-way radio) and a transceiver (the transmit & receive station that sends the signal over airwaves), the following elements must be relayed:
- Audio, in the form of voice, tones or noise.
- The Push To Talk (PTT) and Carrier Operated Relay (COR) signals.
 |
|
Voice over IP |
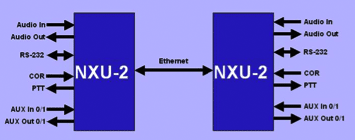
The PTT signal is sent by the radio console to set the transceiver in transmit mode and COR signal, sent by the transceiver sets the 2-way radio in receive mode. In the absence of a COR signal, the 2-way radio uses Voice Operated Xmit (VOX) to detect an incoming audio signal. In addition to the above, the following can also be required:
- RS-232 signal
- Auxiliary (0/1) signal
 |
|
Radio over IP |
Voice-Grade Leased Lines
Voice-Grade Leased Lines are regularly used in public safety land-mobile radio systems as dedicated baseband communication links between two remote points. Leased Lines are also known as: Tie Lines, Wirelines, Dedicated Line, Private Line and Bell 3002.
Unlike dialup voice-grade switched-circuit PSTN telephone lines, Leased Lines provide 24-hour, full-period connectivity and reliability.
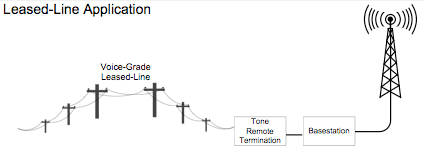
Advantages of Leased Lines:
- 1:1 bandwidth ratio guarantee
- 100% unshared access to stated capacity
- Unambiguous link is relatively secure
These are important requirement of public safety land-mobile radio systems because communications must be ensured at all times in case of emergency.
Disadvantages of Leased Lines:
- Cost is nearly proportional to the distance between each point and can range between $400 to $2000 per month per line.
- User must pay for service even during low-capacity demand
- Lack of flexibility
Alternatives
Products such as the Raytheon NXU-2 RoIP router work flawlessly over our iDirect metered service and completely eliminate the need for Voice-Grade Leased Line. The NXU-2 relays Audio, PTT, COR, RS-232 and Aux 0/1 signals between the Audio Console and the Transceiver over an IP network.
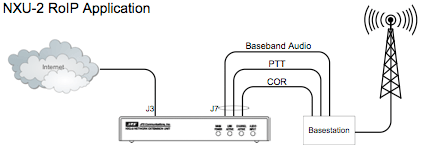
Various voice compression settings are available on the RoIP router to make the most efficient use of bandwidth, but even at its highest data rate, usage remains low.
Available voice compression settings:
- GSM--13 Kbps, suitable for voice communications only (not recommended for tone signaling). This method offers the greatest compression with reasonable voice quality.
- ADPCM--16Kbps, suitable for voice or tone signaling. This method offers good voice compression, but the voice quality is lower than other compression methods.
- ADPCM--24Kbps, suitable for voice or tone signaling. This method offers less compression than ADPCM 16Kbps, but the voice quality is better.
- ADPCM--32Kbps, suitable for voice or tone signaling. Offers even less than 24Kbps compression, but the voice quality is the best of the ADPCM compression types.
- PCM--64Kbps, suitable for voice or tone signaling. Offers the highest quality of all compression methods, but provides the least compression. Not recommended over V-Sat links.
Bandwidth requirements for the above settings are:
- GSM13: 32.5Kbps (16.25Kbps Up, 16.25Kbps Down) + Baud rate of RS-232 port
- ADPCM16: 40Kbps (20Kbps Up, 20Kbps Down) + Baud rate of RS-232 port
- ADPCM24: 60Kbps (30Kbps Up, 30Kbps Down) + Baud rate of RS-232 port
- ADPCM32: 80Kbps (40Kbps Up, 40Kbps Down) + Baud rate of RS-232 port
- PCM64: 160Kbps (80Kbps Up, 80Kbps Down) + Baud rate of RS-232 port
One hour of activity (without RS-232 activity):
- GSM13: 14.28 Mbytes
- ADPCM16: 17.6 Mbytes
- ADPCM24: 26.37 Mbytes
- ADPCM32: 35.2 Mbytes
- PCM64: 70.30 Mbytes
Additional Information
For more information on the Raytheon NXU-2 RoIP router, please visit the Raytheon site.
You can also download the following white papers in PDF format:
- RoIP versus VoIP
- Using the NXU-2 to eliminate voice grade leased lines
- Bandwidth Calculations for the NXU-2
Radio over IP Acronyms
- ADPCM: Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation, is a form of Voice Coding and Decoding algorithm used by the NXU
- COR: Carrier Operated Relay, is a signal from a receiver that indicates when a carrier or signal is being received and that the receiver is unsquelched.
- GSM: Global System for Mobile Communications, is a form of Voice Coding and Decoding algorithm used by the NXU
- ISDN: Integrated Services Digital Network, is a digital telephone connection that uses digital signals instead of analogue signals to handle the transfer of signaling and speech.
- NXU: Network Extension Unit, is a device used to connect a DSP-1 module or a land mobile radio device over an IP-based network. The unit creates a network link that passes both voice and control signals in the form of RoIP.
- PCM: Pulse Code Modulation, is a form of Voice Coding and Decoding algorithm used by the NXU
- PSTN: Public Switch Telephone Network, which refers to the international telephone system based on copper wires and switched circuits for carrying analog voice data.
- PTT: Push-to-Talk, A signal to a radio transmitter, which controls the actual transmission of radio frequency energy over the air.
- RoIP: Radio over Internet Protocol, (compared to VoIP) not only converts voice to a digital format that can be sent over the Internet or other IP based network, but also convert PTT and COR control signals that are essential for seamless for radio interoperability. Also include are extra delay and jitter compensation.
- TCP/IP: Transport Control Protocol / Internet Protocol, is an additional layer to the Internet Protocol, which ensures delivery of packets, sent across the network. It can handle situations such as lost packets or packets arriving out of order.
- VOCODER: Voice Coder / Decoder, is an algorithm use by the NXU that reduces speech signals to slowly varying signals transmittable over TCP/IP networks to conserve network bandwidth. VoIP: Voice over Internet Protocol, is a method of sending voice communications across a digital network.


